
In the quest for sustainable and renewable energy solutions, solar power systems provide both household and commercial entities with a reliable source of green energy. Solar power harnesses the sun’s energy, converting it into electricity to power everything from small homes to large commercial businesses. This transformation is facilitated through various types of solar systems, each tailored to meet specific needs and circumstances. Here, we delve into the three different solar power systems alongside a brief exploration of different solar panel installations.
What Is Grid-tied Solar System?
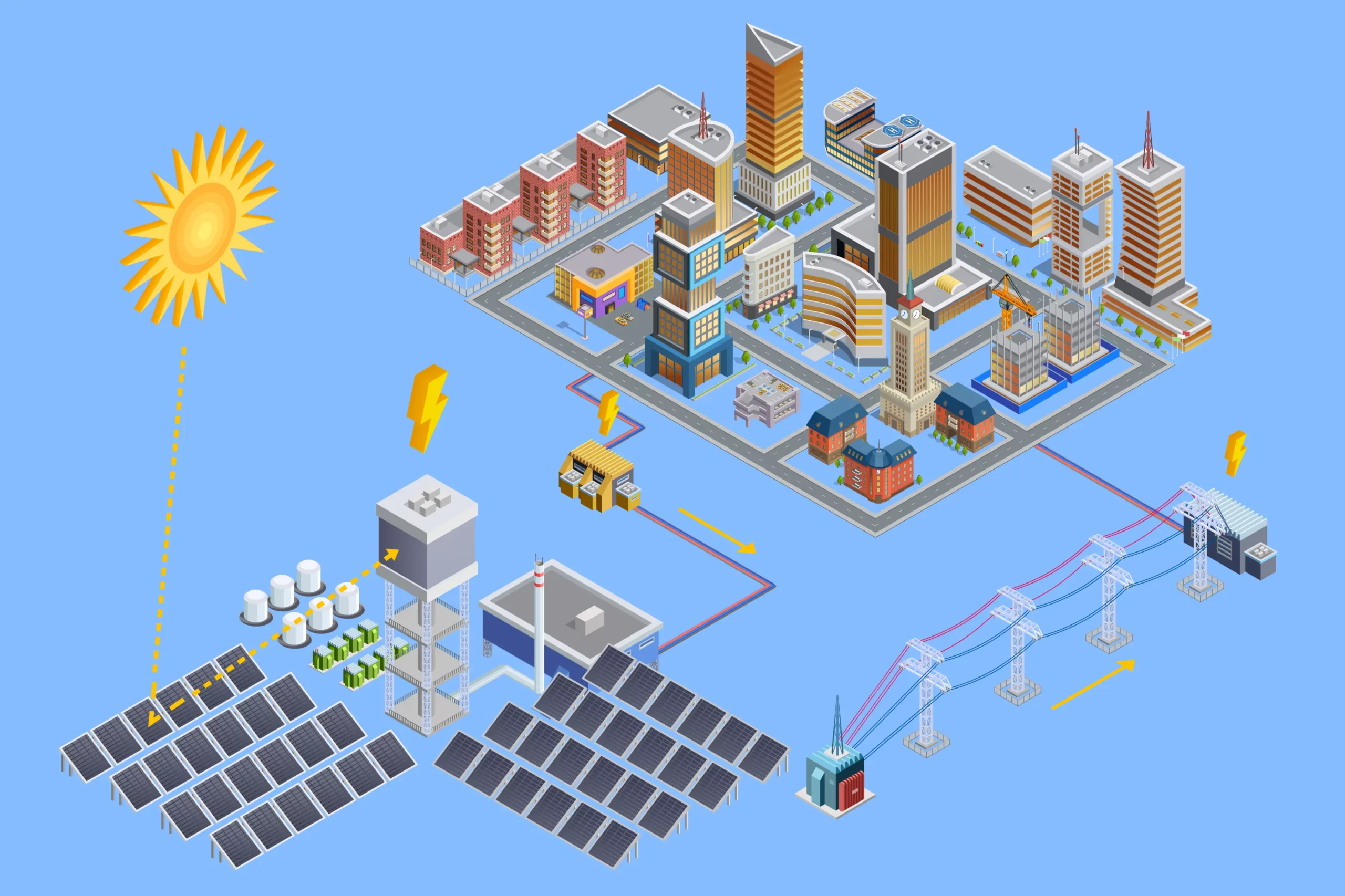

The Grid-tied solar system is the most prevalent form of solar power for commercial and home globally, connecting with the local utility grid. This configuration is particularly appealing for both residential and commercial setups, enabling them to produce their electricity via solar panels. One of the system’s key features is its ability to use the grid as a backup power source during periods when solar production is not sufficient to meet the property’s energy demands. This dual-functionality helps promote a more sustainable integration with existing power infrastructure.
Advantages of Grid-tied Solar System
- One of the primary advantages of Grid-tied solar systems lies in their financial benefits. The concept of net metering allows property owners to feed excess generated electricity back into the grid, effectively reducing or even negating their electricity bills. This symbiotic relationship between solar producers and the utility grid creates a mutually beneficial scenario, encouraging more individuals and businesses to invest in solar technology.
- By leveraging the sun’s renewable energy, Grid-tied systems play a role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and dependency on fossil fuels. This transition to clean energy sources is crucial in combating climate change and promoting the environment. The adoption of solar power also aligns with global sustainability goals, pushing for a greener, more sustainable energy future.
- Compared to their off-grid counterparts, Grid-tied solar systems require significantly fewer components, making them easier and less costly to maintain. The absence of batteries in a Grid-tied setup simplifies the system, reducing the need for regular upkeep and potential replacement parts. This simplicity ensures a longer lifespan for the core components and a more straightforward operation.
Grid-tied Solar System Components
- Solar Panels: The heart of any solar power system, these panels capture sunlight and convert it into electrical energy. Modern panels are highly efficient and capable of generating significant amounts of power even on days with limited sunlight.
- Inverter: This critical component transforms the DC electricity produced by the solar panels into AC electricity, which is the standard form used in homes and businesses. Inverters also monitor the system’s performance and ensure that the electricity generated is safe and compatible with the grid and home appliances.
- Metering System: Essential for implementing net metering, this system tracks the amount of electricity exported to and imported from the grid. Advanced metering systems can provide detailed insights into a system’s performance, including real-time data on production and consumption, allowing for more informed energy management decisions.
- Grid Interface: Facilitates the connection between the solar panel system and the utility grid, ensuring that the transition of power is smooth and compliant with local regulations and grid standards.
- Mounting Hardware: Durable frames and supports that secure the solar panels either on the roof or on the ground. This hardware is designed to withstand environmental factors such as wind and snow, ensuring the panels remain optimally positioned for maximum sun exposure.
What Is an Off-Grid Solar System?
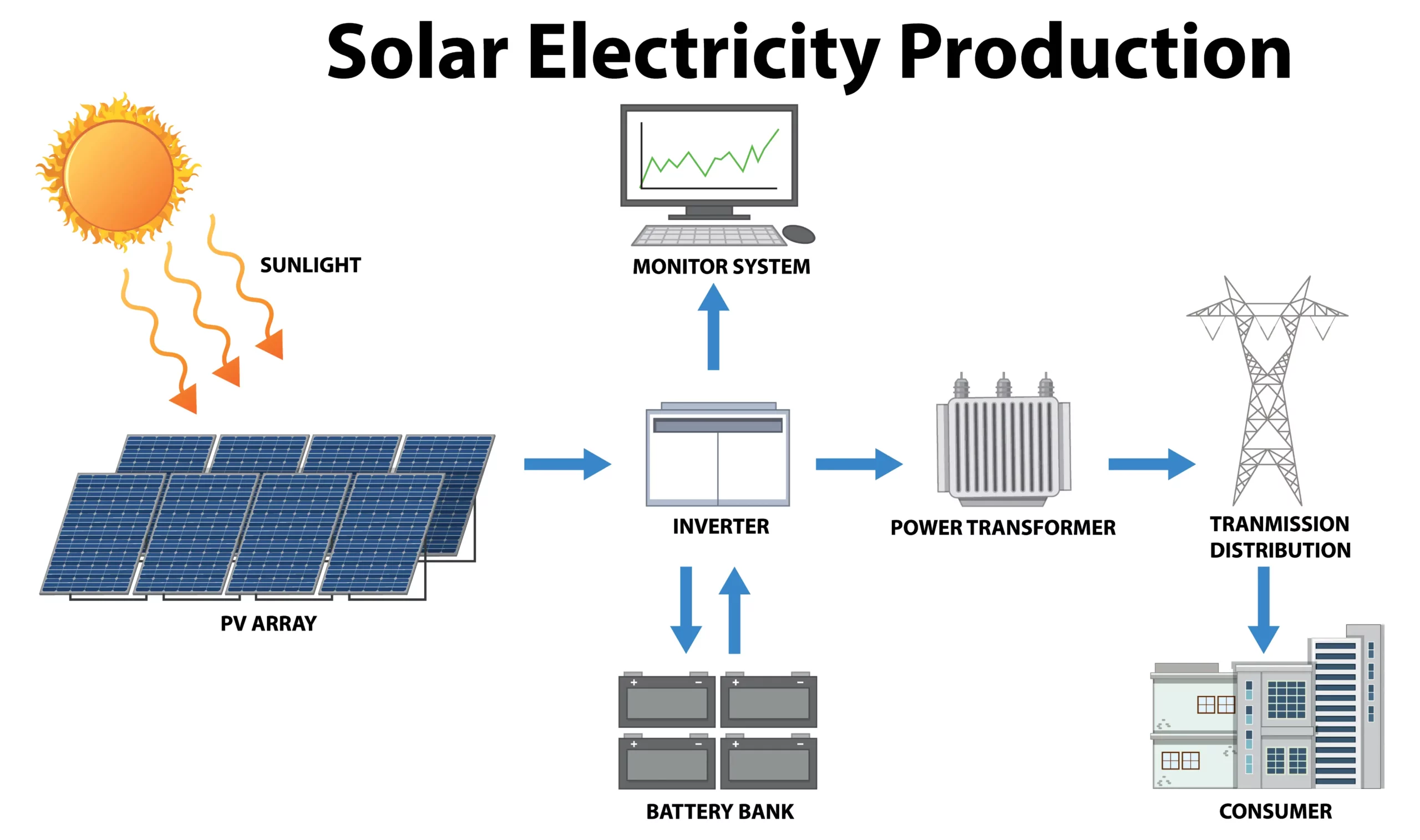
An Off-Grid solar system operates independently of the local utility grid, presenting an ideal solution for locations that lack reliable grid access. These systems are specifically designed to be self-sufficient, requiring careful planning and implementation to ensure they generate sufficient power throughout the year, especially during periods of low sunlight. This autonomy makes off-grid systems especially appealing for remote or rural areas where grid connection is either impossible or prohibitively expensive.
Advantages of Off-Grid Solar System
- The foremost advantage of an off-grid solar system is the complete independence it offers from the utility grid. This off-grid solar system is particularly valuable in remote locations, providing a reliable and constant energy supply without the need for grid connectivity.
- After the initial setup costs, the electricity generated by an off-grid system is entirely free. This translates to significant long-term savings and protection from rising energy prices for homeowners and businesses.
- Utilizing the sun’s power, off-grid systems contribute positively to the environment by significantly reducing the reliance on fossil fuels and lowering carbon emissions. This clean, renewable source of energy aligns with global efforts to combat climate change and promotes sustainability.
Off-Grid Solar System Components
- Solar Panels: These are the primary source of electricity generation in an off-grid system, capturing solar energy and converting it into electrical power.
- Batteries: Essential for storing surplus electricity for use during times when solar production is low, such as at night or on cloudy days. Modern battery technologies offer high storage capacities and longevity.
- Inverter: Converts the DC electricity stored in batteries into AC power, making it usable for standard home and business appliances.
- Backup Generator: Often included in off-grid systems for additional reliability, especially during prolonged periods of insufficient sunlight.
- Energy Management System (EMS): Monitors and optimizes energy production, consumption, and storage, ensuring the efficient use of resources. Integral to this system, the Charge Controller strengthens the EMS by managing the flow of electricity to and from the battery bank, preventing overcharging and significantly extending battery life.
What Is a Smart Grid?
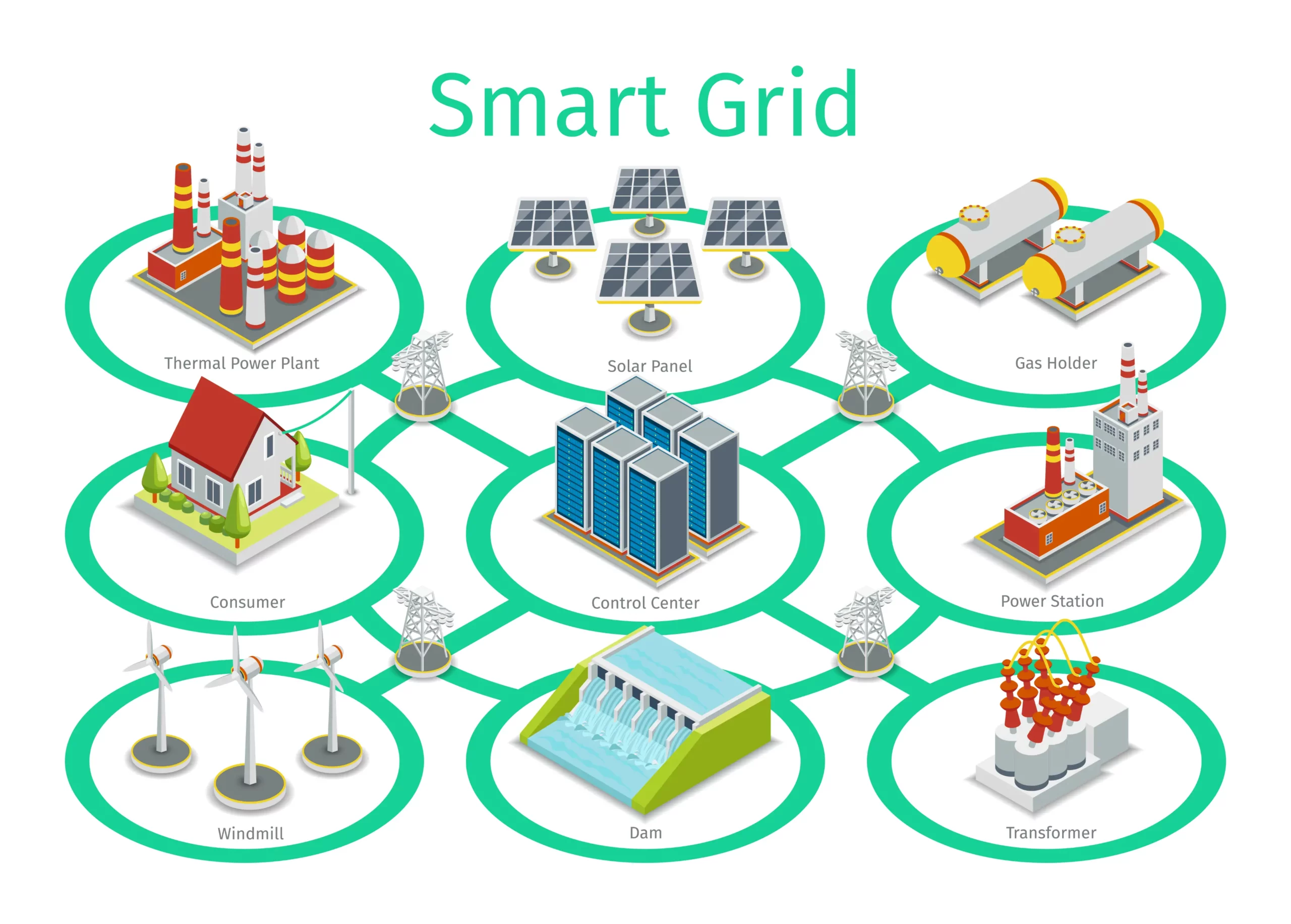
A Smart Grid is an advanced electrical grid enhanced with information and communication technologies, enabling real-time monitoring and management of energy flow. This modern grid system facilitates the efficient distribution and consumption of electricity from various sources, including renewable energy. It is designed to optimize the performance of the entire electricity supply chain, from generation to consumption, improving reliability, security, and sustainability of energy resources.
Advantages of Smart Grid
- By intelligently managing energy supply and demand, smart grids significantly reduce energy wastage, ensuring that electricity is used optimally, with less loss in transmission and distribution. Smart grids can also reroute power as needed to avoid overloading specific network areas, leading to more efficient grid operation overall.
- Smart grids are adept at integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, into the energy mix. They can manage the variable nature of renewable energy production, ensuring that the grid remains stable even when renewable generation fluctuates.
- Smart grids empower consumers by providing them with real-time data on energy usage and costs through advanced metering infrastructure. This information, often accessible via smartphone apps or online platforms, allows consumers to make informed decisions about their energy consumption, encouraging energy-saving behaviors and enabling more active participation in energy markets.
- The smart grid supports dynamic pricing models, where electricity pricing can vary in real time based on supply and demand. This flexibility allows consumers to adjust their usage according to price signals, potentially using more energy when it is cheaper and less during peak demand times. Such pricing models incentivize energy efficiency and can lead to cost savings for consumers, while also helping to balance the grid during times of high demand.
Smart Grid Components
- Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI): These smart meters measure and communicate energy usage in real-time. They provide a two-way communication channel between consumers and utilities, enabling dynamic pricing and detailed consumption tracking. It also supports the remote management of energy services, such as connecting or disconnecting power and identifying specific areas of energy waste.
- Distribution Automation: These automated control systems significantly improve the reliability and efficiency of electricity distribution. By quickly identifying and isolating faults, they minimize outages and ensure a steady electricity supply.
- Renewable Energy Sources Integration: These systems integrate energy from solar, wind, and other renewable sources into the grid. They manage the variability and intermittency of renewable energy, ensuring that the grid remains stable and reliable even when large amounts of renewable energy are introduced.
- Energy Storage Systems: Beyond just batteries, these technologies encompass a range of solutions for storing excess energy, from pumped hydro storage to flywheels and beyond. They release stored energy to the grid to prevent blackouts and reduce reliance on peak-time power plants.
- Communication Network: This robust and secure network ensures communication between all grid components, utilities, and consumers. It supports a vast array of applications, from the transmission of real-time energy usage data to the remote control of grid devices and consumer appliances.
Types of Solar Panel Installations
Beyond the categorization by connectivity and energy independence, solar power systems can also vary based on their installation type. These include:
- Rooftop Solar: A highly adaptable option, rooftop solar installations capitalize on unused space and potentially increase property values. The rooftop solar is especially effective in urban areas where land is scarce. These systems can be designed to blend with the building’s architecture, making them aesthetically pleasing as well as functional.
- Ground-mounted Solar: These systems allow optimal panel orientation and angle adjustment to maximize solar energy capture and enhance overall efficiency. A specialized subset of ground-mounted systems includes track-mounted solar, which elevates energy production to new heights. By automatically adjusting the panels to follow the sun’s path, track-mounted systems significantly outperform stationary setups, especially in locations with considerable sunlight variability throughout the day.
- Floating Solar: Floating systems are a testament to innovation, reducing water evaporation while generating clean energy. The floating solar is particularly suited for areas with limited land but abundant calm water bodies. The cooling effect of water increases panel efficiency, offering a unique advantage over land-based installations.
- Carport Solar: Carport installations turn parking lots into power plants, providing shade and protection for vehicles while generating electricity. This dual-purpose solution is particularly appealing for commercial entities with large parking areas, offering a sustainable addition to corporate social responsibility efforts.
- Wall-mounted Solar: Wall-mounted panels offer a solution for buildings with limited roof space or unsuitable roof orientations. They can be installed to capture sunlight at different times of the day, depending on the building’s orientation, making them a flexible option for maximizing solar energy usage.
BECIS Onsite Solar Solution

Onsite solar solutions are revolutionizing how businesses and household areas approach energy consumption and sustainability. These solutions offer significant savings on energy costs while reducing emissions, aligning with global efforts to combat climate change. With options ranging from rooftop and floating solar power plants to carport and ground-mounted installations, these systems are designed to meet diverse needs. The integration of advanced technologies like highly efficient PV modules, multi-MPPT inverters, cloud-based IoT for real-time monitoring, and comprehensive power management solutions ensures operation and maximum energy output.
BECIS’ Onsite Solar Solution represents a cutting-edge innovation in solar energy, offering a comprehensive package that includes the design, installation, and management of solar power systems. This solution is tailored to meet the specific solar power needs of homes and businesses, ensuring optimal performance and sustainability. BECIS’ commitment to stringent environmental, health, and safety standards further underscores the reliability and ethical considerations of its onsite solar solutions.
Check out our onsite solar virtual tour to have a deep understanding of different kinds of solar installation.

In summary, incorporating the mentioned types of commercial and home solar systems offers economic benefits through energy savings and incentives. The advancements in solar technology and the availability of various installation types, coupled with innovative solutions like BECIS’ Onsite Solar Solution, underscore the versatility and accessibility of solar power for a wide range of applications.
About BECIS
BECIS is a sustainable Energy as a Service (EaaS) solution provider. We offer a range of services, including solar energy, bioenergy, cooling, heating, waste heat recovery, compressed air, and energy analytics. Contact us today to learn more about our services.





























Recent Comments